Aurora Program for Master and PhD students
Apply now for the Aurora excellence fellowship program for visiting Master and PhD students! Travel expenses and accommodation will be fully covered. More information in the “Openings 2026” menu.

Welcome to the Quantum World!
Our group travelled to the Vienna City Hall for “Willkommen Quantenwelt” celebrating 100 years of quantum science. Thanks to Quantum Science Austria and collaborators for organizing this fantastic event!

2025 Group Openings!
We are happy to announce that our dipolar quantum gas group has an Academy Scientist + Postdoc and PhD positions open for 2025!

“Dance your PhD 2025” contest by Science and AAAS
Congratulations to our PhD student Arfor, who turned our research topics into a dazzling music video!

Vortices in a supersolid
2024’s Biggest Breakthroughs in Physics: Our research on the observation of vortices in a dipolar supersolid featured by Quanta magazine!

Austrian of the Year 2024
Francesca was crowned as the ‘Austrian of the Year’ in the research category at the Austria 24 gala by Die Presse!
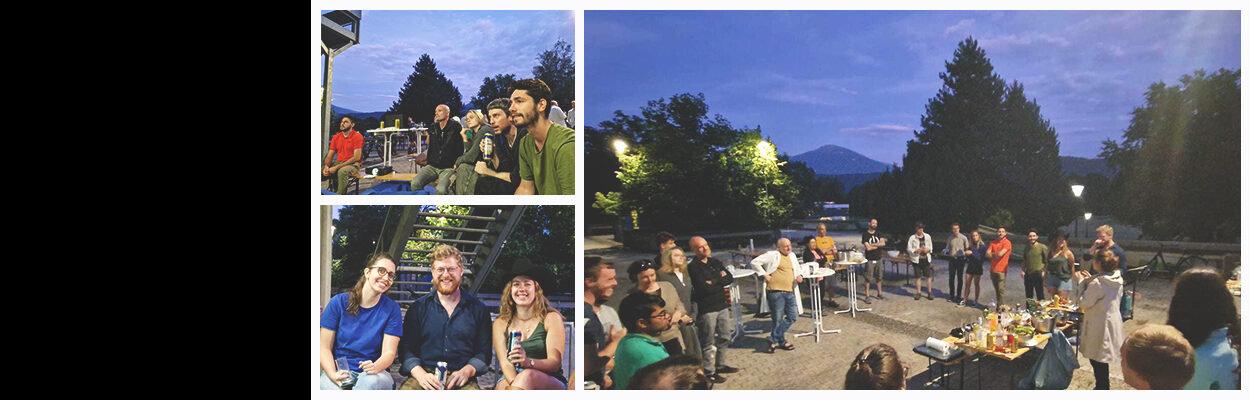

Summer BBQ
Our 2024 Summer BBQ took place on the 24th of June and celebrated the many different achievements of the group!
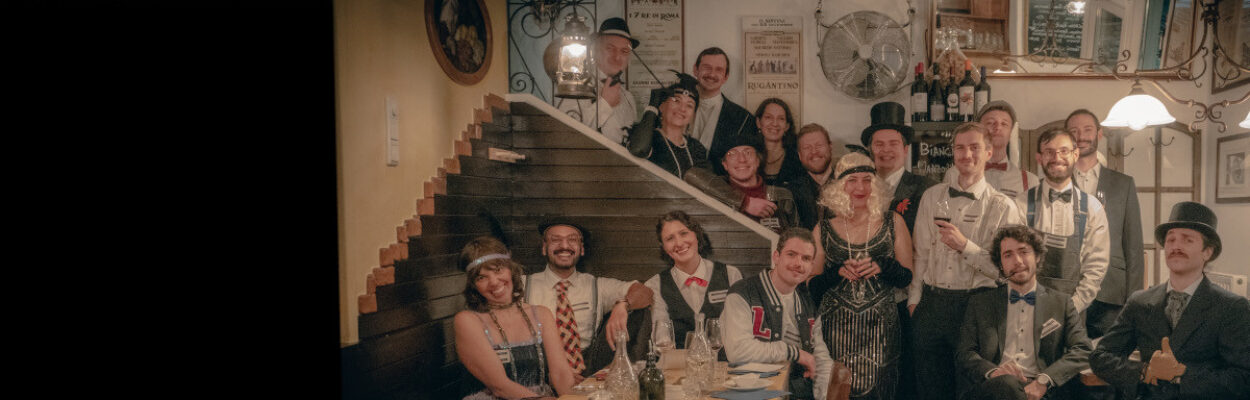

Murder Mystery Dinner
Our 2024 group dinner took place on the 18th of January at CasoinN da Giorgio restaurant, with a 1920’s Murder Mystery theme!
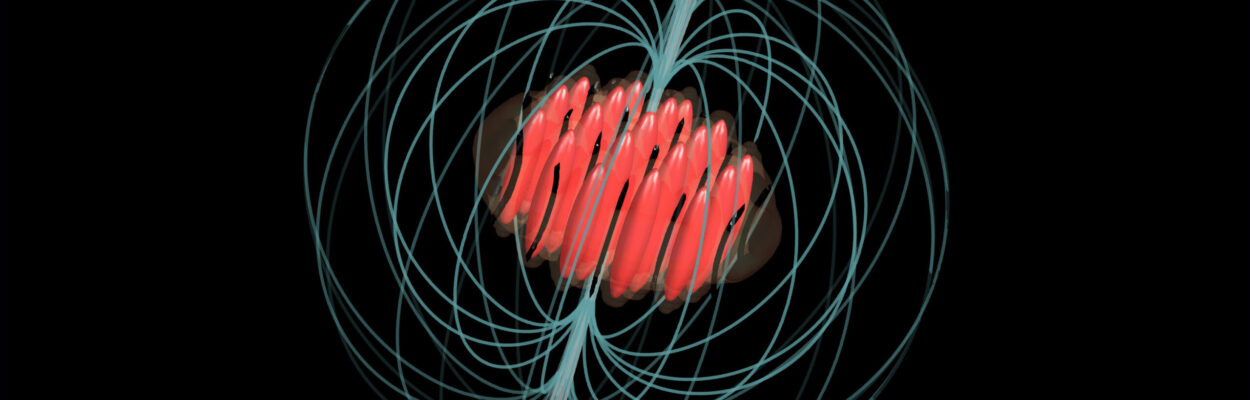
Glitches in supersolids: links between neutron stars and quantum matter
By emulating the connection between a rotating supersolid phase and an external solid phase, we were able to replicate “glitches” – sudden jumps in the solid angular momentum driven by quantum vortices leaving the supersolid.
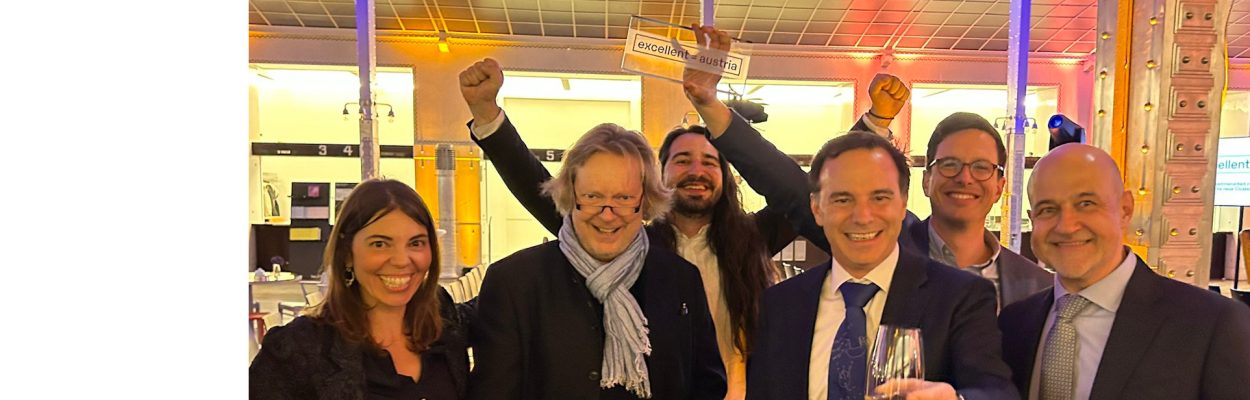

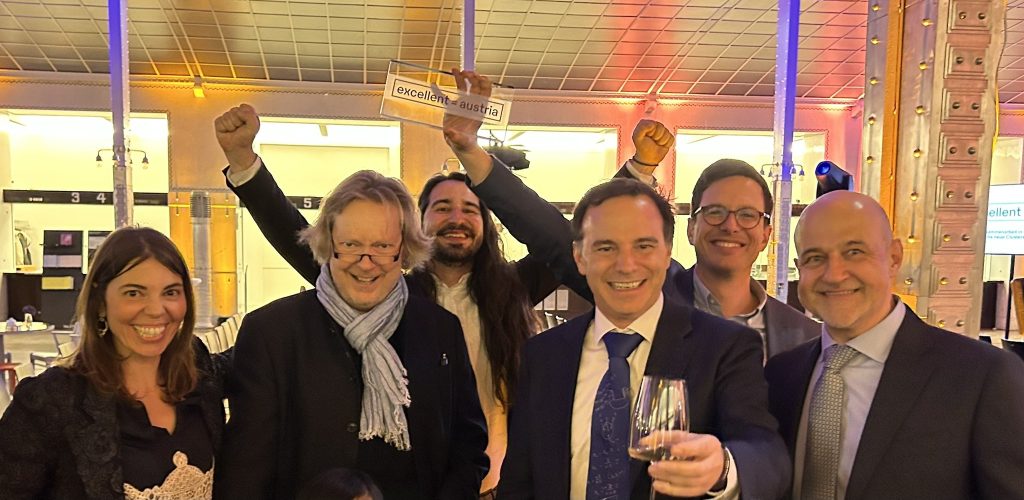
Cluster of Excellence Quantum Science Austria granted
Three Clusters of Excellence in Innsbruck have been funded! With highly endowed clusters of excellence, the Austrian Science Fund FWF creates Austrian flagships of basic research. The University of Innsbruck will coordinate the Cluster of Excellence for Quantum Sciences.
Our group studies dipolar quantum gases made of Erbium (Er) and Dysprosium (Dy) atoms. These extraordinarily magnetic species are a powerful new resource for reaching quantum simulation with strong connectivity, in which each atom is coupled to the other over long distances, and exploring exotic phases of matter that have no classical counterpart.
We have four labs: the ERBIUM LAB, where Er was Bose condensed for the first time ever; the Er-Dy LAB, which studies quantum dipolar mixtures under a quantum-gas microscope; the T-REQs LAB, where we trap Er atoms in arrays of optical tweezers for Rydberg physics; and the Dy-Yb LAB, currently under construction – this new experimental apparatus will be used to study many-body phases of highly-magnetic dysprosium and of mixtures with non-magnetic ytterbium. The Theory Group completes our team studying and predicting dipolar phenomena in dipolar quantum gases and mixtures.
The group, led by Francesca Ferlaino, is jointly located at the Institute for Experimental Physics (IExP) of the University of Innsbruck and at the Institute for Quantum Optics and Quantum Information (IQOQI) of the Austrian Academy of Sciences, and it is part of the Innsbruck Center for Ultracold Atoms and Quantum Gases.
Follow our group’s updates on Bluesky  and LinkedIn
and LinkedIn  !
!
News from the labs
Our publication on the first-time observation of roton quasiparticles in quantum gases was chosen by the editors of Nature Physics as one of their favorite papers of the past 15 years. To mark the anniversary of the journal, the most important works in the various disciplines of physics are presented.
Keep Reading ...
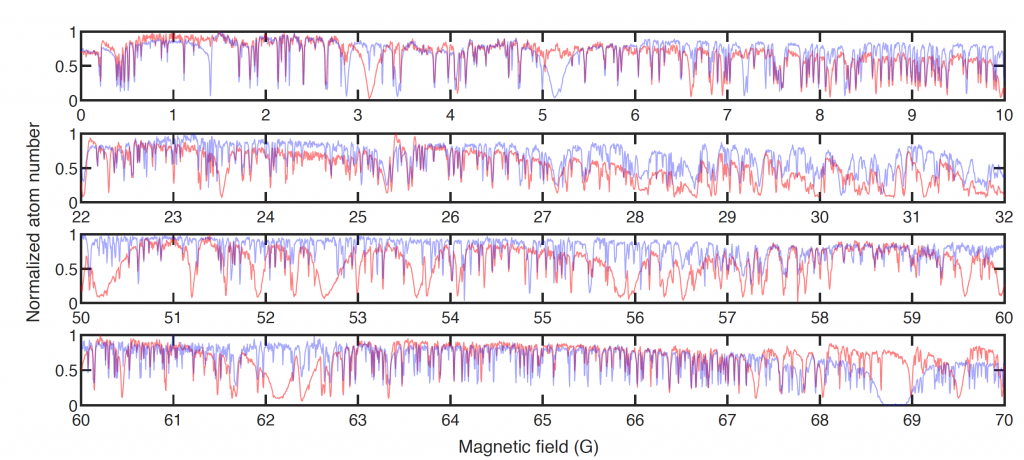
A key step in creating controlled interactions in dipolar quantum mixtures is the characterization of interspecies Feshbach resonances.
Keep Reading ...
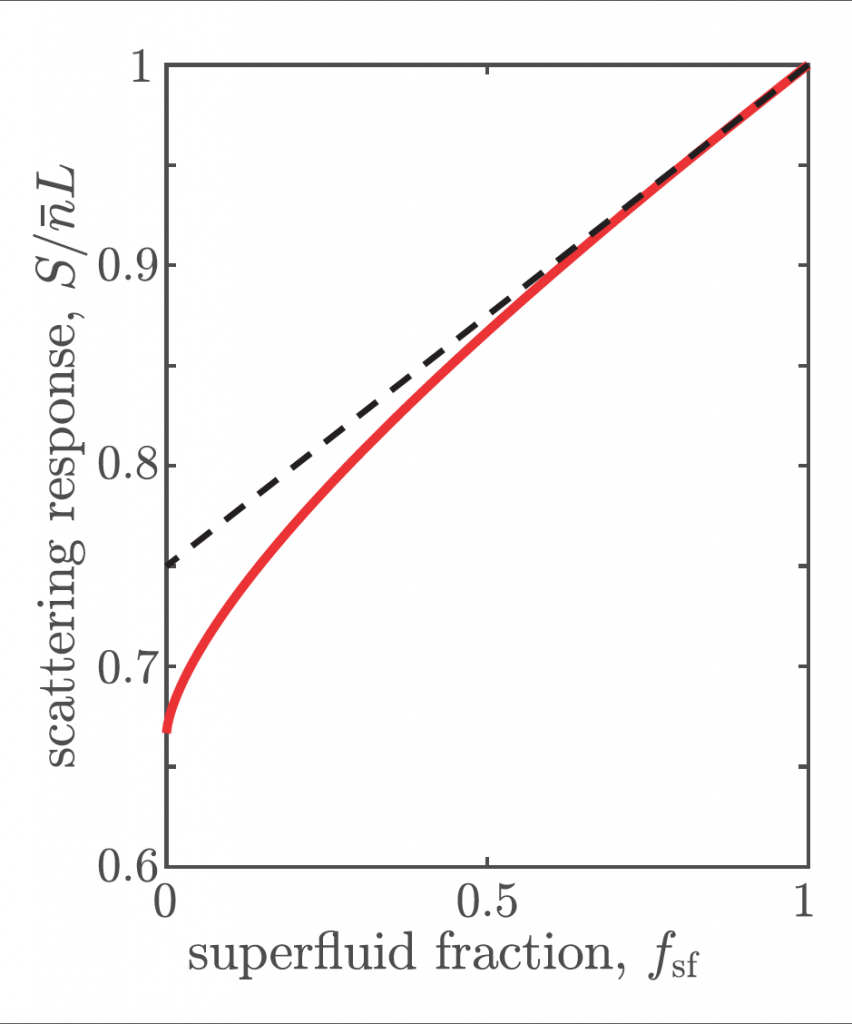
Congratulation to Lauriane Chomaz on the publication of her paper in Phys. Rev. A. In this work, Lauriane investigates the general relationships existing between the density contrast, the superfluid fraction, and the response to a high-energy scattering probe of density-modulated states within a classical-field approach.
Keep Reading ...
Group news
May 10-12. 2023 - Unravelling quantum many-body physic with long-range interacting platforms
Keep Reading ...
Three Clusters of Excellence in Innsbruck have been funded! With highly endowed clusters of excellence, the Austrian Science Fund FWF creates Austrian flagships of basic research. The University of Innsbruck will coordinate the Cluster of Excellence for Quantum Sciences.
Keep Reading ...
Welcome and goodbye
Welcome to Antonio Ortu, who is joining the T-REQS lab as a postdoc.
Keep Reading ...
Welcome to Théo Mezieres, who is joining Eribum lab for his Masters' internship.
Keep Reading ...
Welcome to Johanna Hennebichler, who has joined the T-Reqs team for her Master Thesis.
Keep Reading ...
 and LinkedIn
and LinkedIn ![]() !
!